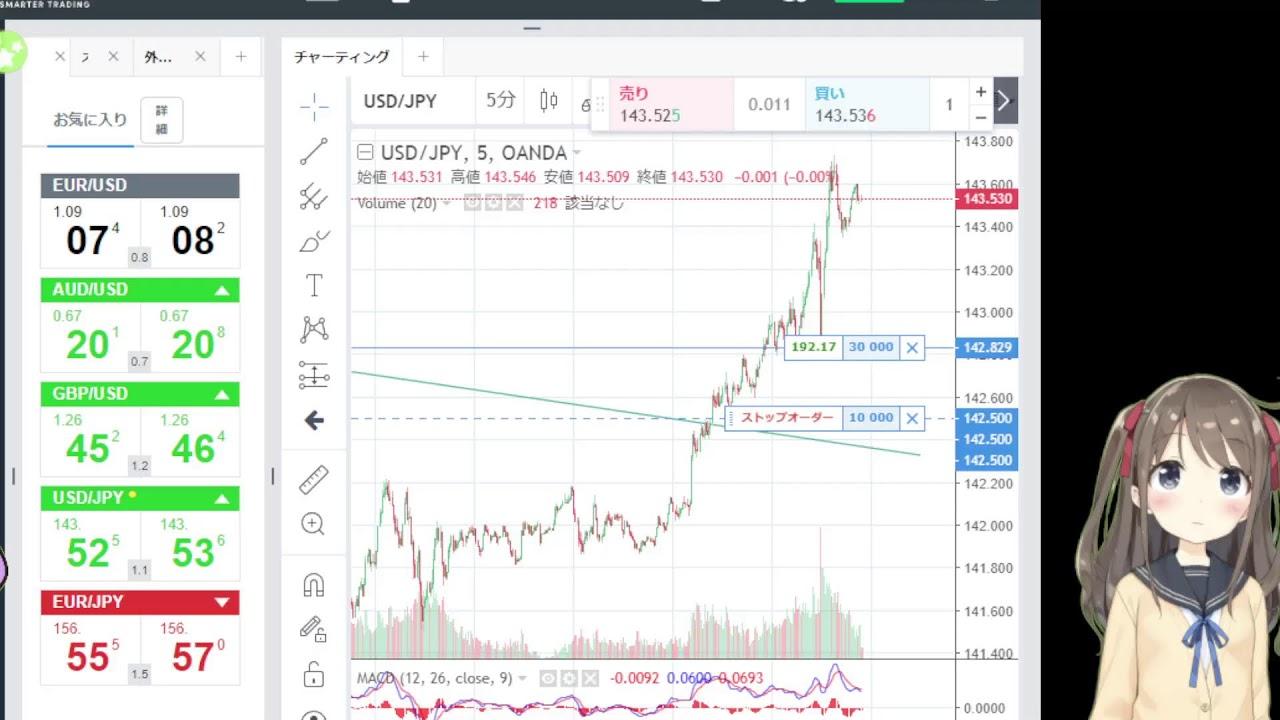
In the realm of forex trading, a "spread" refers to the difference between the bid (selling) and ask (buying) prices of a currency pair. The bid price is the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a specific currency, while the ask price is the amount a seller is asking for that same currency. The spread is essentially the cost of executing a trade and represents the broker's profit in most cases.
Here's a breakdown of the components:
- Bid Price: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a currency pair.
- Ask Price: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept for the same currency pair.
- Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices. It is typically measured in pips (percentage in point), which is the smallest price move that a given exchange rate can make based on market convention.
A tight spread is generally preferable for traders, as it reduces the cost of entering and exiting positions. Brokers may offer fixed or variable spreads, and the choice between the two depends on the trader's preferences and trading strategy.
Low spreads are often associated with high liquidity and competitive market conditions. In contrast, wider spreads may occur during periods of low liquidity, market volatility, or when trading exotic currency pairs.
Understanding spreads is crucial for traders because it directly affects the profitability of their trades. It's essential to factor in the spread when calculating potential profits or losses and to be aware of how it can change under different market conditions. Traders should choose brokers that offer transparent pricing and fair spreads to optimize their trading experience.